Complete Blood Count (CBC)
Test Overview
A complete blood count (CBC) gives important information about the kinds and numbers of cells in the blood, especially red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. A CBC helps your doctor check any symptoms that you may have, such as weakness, fatigue, or bruising. A CBC also helps him or her diagnose conditions, such as anemia, infection, and many other disorders.
A CBC test usually includes:
- White blood cell (WBC, leukocyte) count.
White blood cells protect the body against infection. If an infection develops, white blood cells attack and destroy the bacteria, virus, or other organism causing it. White blood cells are bigger than red blood cells but fewer in number. When a person has a bacterial infection, the number of white cells rises very quickly. The number of white blood cells is sometimes used to find an infection or to see how the body is dealing with cancer treatment.
- White blood cell types (WBC differential).
The major types of white blood cells are neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils. Immature neutrophils, called band neutrophils, are also part of this test. Each type of cell plays a different role in protecting the body. The numbers of each one of these types of white blood cells give important information about the immune system. Too many or too few of the different types of white blood cells can help find an infection, an allergic or toxic reaction to medicines or chemicals, and many conditions, such as leukemia.
- Red blood cell (RBC) count.
Red blood cells carry oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body. They also carry carbon dioxide back to the lungs so it can be exhaled. If the RBC count is low (anemia), the body may not be getting the oxygen it needs. If the count is too high (a condition called polycythemia), there's a chance that the red blood cells will clump together and block tiny blood vessels (capillaries). This also makes it hard for your red blood cells to carry oxygen.
- Hematocrit (HCT, packed cell volume, PCV).
This test measures the amount of space (volume) red blood cells take up in the blood. The value is given as a percentage of red blood cells in a volume of blood. For example, a hematocrit of 38 means that 38% of the blood's volume is made of red blood cells. Hematocrit and hemoglobin values are the two major tests that show if anemia or polycythemia is present.
- Hemoglobin (Hgb).
The hemoglobin molecule fills up the red blood cells. It carries oxygen and gives the blood cell its red color. The hemoglobin test measures the amount of hemoglobin in blood. It's a good measure of how well the blood can carry oxygen throughout the body.
- Red blood cell indices.
There are three red blood cell indices: mean corpuscular volume (MCV), mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH), and mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC). They are measured by a machine, and their values come from other measurements in a CBC. The MCV shows the size of the red blood cells. The MCH value is the amount of hemoglobin in an average red blood cell. The MCHC measures the concentration of hemoglobin in an average red blood cell. These numbers help in the diagnosis of different types of anemia. Red cell distribution width (RDW) can also be measured. It shows if the cells are all the same or different sizes or shapes.
- Platelet (thrombocyte) count.
Platelets (thrombocytes) are the smallest type of blood cell. They are important in blood clotting. When bleeding occurs, the platelets swell, clump together, and form a sticky plug that helps stop the bleeding. If there are too few platelets, uncontrolled bleeding may be a problem. If there are too many platelets, there is a chance of a blood clot forming in a blood vessel. Also, platelets may be involved in hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis).
- Mean platelet volume (MPV).
Mean platelet volume measures the average amount (volume) of platelets. MPV is used along with platelet count to diagnose some diseases. If the platelet count is normal, the MPV can still be too high or too low.
Why It Is Done
A CBC may be done as part of a regular physical exam. There are many other reasons that a doctor may want this blood test, including to:
- Find the cause of symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, fever, bruising, or weight loss.
- Check for anemia.
- See how much blood has been lost if there is bleeding.
- Diagnose polycythemia.
- Check for an infection.
- Diagnose diseases of the blood, such as leukemia.
- Check how the body is dealing with some types of drug or radiation treatment.
- Check how abnormal bleeding is affecting the blood cells and counts.
- Screen for high and low values before a surgery.
- See if there are too many or too few of certain types of cells. This may help find other conditions. For instance, too many eosinophils may be a sign of an allergy or asthma.
A blood count can give valuable information about the general state of your health.
How To Prepare
In general, there's nothing you have to do before this test, unless your doctor tells you to.
How It Is Done
A health professional uses a needle to take a blood sample, usually from the arm.
Watch
How It Feels
When a blood sample is taken, you may feel nothing at all from the needle. Or you might feel a quick sting or pinch.
Risks
There is very little chance of having a problem from this test. When a blood sample is taken, a small bruise may form at the site.
Results
Normal
Each lab has a different range for what's normal. Your lab report should show the range that your lab uses for each test. The normal range is just a guide. Your doctor will also look at your results based on your age, health, and other factors. A value that isn't in the normal range may still be normal for you.
Normal values for the complete blood count (CBC) tests depend on age, sex, how high above sea level you live, and the type of blood sample. Your doctor may use all the CBC values to check for a condition. For example, the red blood cell (RBC) count, hemoglobin (Hgb), and hematocrit (HCT) are the most important values needed to tell whether a person has anemia. But the red blood cell indices and the blood smear also help with the diagnosis and may show a possible cause for the anemia.
To see if the white blood cell (WBC, leukocyte) count is good and how the cells look on the smear, your doctor will look at both the number (WBC count) and the WBC differential. To see whether there are too many or too few of a certain type of cell, your doctor will look at the total count and the percentage of that particular cell. There are normal values for the total number of each type of white cell.
Pregnancy can change these blood values. Your doctor will talk with you about normal values during each trimester of your pregnancy.
Normal: | Blood cells are normal in shape, size, color, and number. |
|---|
High values
- Red blood cells (RBC).
- Conditions that cause high RBC values include smoking, exposure to carbon monoxide, long-term lung disease, kidney disease, some cancers, certain forms of heart disease, alcohol use disorder, liver disease, a rare disorder of the bone marrow (polycythemia vera), and a rare disorder of hemoglobin that binds oxygen tightly.
- Conditions that affect the body's water content can also cause high RBC values. These conditions include dehydration, diarrhea or vomiting, excessive sweating, and the use of diuretics. The lack of fluid in the body makes the RBC volume look high. This is sometimes called spurious polycythemia.
- White blood cells (WBC, leukocytes).
- Conditions that cause high WBC values include infection, inflammation, damage to body tissues (such as a heart attack), severe physical or emotional stress (such as a fever, injury, or surgery), kidney failure, lupus, tuberculosis (TB), rheumatoid arthritis, malnutrition, leukemia, and diseases such as cancer.
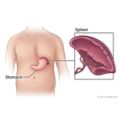
- The use of corticosteroids, underactive adrenal glands, thyroid gland problems, certain medicines, and removal of the spleen can also cause high WBC values.
- Platelets.
- High platelet values may be seen with bleeding, iron deficiency, some diseases like cancer, or problems with the bone marrow.
Low values
- Red blood cells (RBC).
- Anemia lowers RBC values. Anemia can be caused by heavy menstrual bleeding, stomach ulcers, colon cancer, inflammatory bowel disease, some tumors, Addison's disease, thalassemia, lead poisoning, sickle cell disease, and reactions to some chemicals and medicines. A low RBC value may also be seen if the spleen has been taken out.
- A lack of folic acid or vitamin B12 can also cause anemia, such as pernicious anemia. This is a problem with absorbing vitamin B12.
- The RBC indices value and a blood smear may help find the cause of anemia.
- White blood cells (WBC, leukocytes).
- Conditions that can lower WBC values include chemotherapy and reactions to other medicines, aplastic anemia, viral infections, malaria, alcohol use disorder, AIDS, lupus, and Cushing's syndrome.
- A large spleen can lower the WBC count.
- Platelets.
- Low platelet values can occur in pregnancy or immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) and other conditions that affect how platelets are made or that destroy platelets.
- A large spleen can lower the platelet count.
Credits
Current as of: May 13, 2023
Author: Healthwise Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Healthwise education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Current as of: May 13, 2023
Author: Healthwise Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Healthwise education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.